Generations of Computer
- First Generation – 1946 – 1955
- Second generation – 1956 – 1965
- Third generation – 1965 – 1975
- Fourth-generation – 1975 – 1985
- Fifth-generation – 1985 onwards
The First Generation
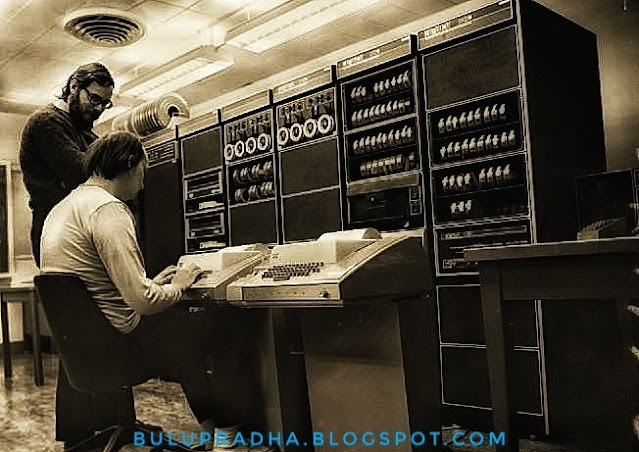
The first generation computer used vacuum tubes for circuitry and magnetic drums for memory, and was often enormous, taking up entire rooms.
They were very expensive to operate and in addition to using a great deal of electricity, generated a lot of heat, which was often the cause of malfunctions.
 |
| ENIAC |
 |
| VACUM TUBE VALA IMAGE |
The First Generation
The first generation computer used vacuum tubes for circuitry and magnetic drums for memory, and was often enormous, taking up entire rooms.
• They were very expensive to operate and in addition to using a great deal of electricity, generated a lot of heat, which was often the cause of malfunctions.
ENIAC
• ENIAC stands for Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer.
• It was the first electronic general-purpose computer.
• Completed in 1946.
• Developed by John Presper Eckert and John W. Mauchly.
EDVAC
• EDVAC stands for Electronic Discrete Variable Automatic Computer.
• The First Stored Program Computer
• Designed by Von Neumann in 1952.
• It has a memory to hold both a stored program as well as data.
Disadvantages of 1st Generation Computer
⦁ The computers were very larger in size
⦁ They consumed a large amount of energy.
⦁ They heated very soon due to thousands of vacuum tubes.
⦁ They were not very reliable.
⦁ Air conditioning is required.
⦁ Constant maintenance was required.
⦁ Not-portable.
⦁ Costly commercial production.
⦁ Very slow speed.
⦁ Limited programming capabilities.
⦁ Used machine language only.
⦁ Used punch card for input.
⦁ Not versatile and less accurate.
The Second Generation
• Transistors replaced vacuum tubes and used them in the second generation of computers.
• One transistor replaced the equivalent of 40 vacuum tubes and its size was 1/200th of the size of the vacuum tube.
• Allowing computers to become smaller, faster, cheaper, more energy-efficient
and more reliable.
Walter Houser Brattain ( February 10, 1902 – October 13, 1987) was an American physicist at Bell Labs who, along with fellow scientists John Bardeen and William Shockley, invented the point-contact transistor in December 1947. They shared the 1956 Nobel Prize in Physics for their invention.
The Third generation
The development of the integrated circuit was the hallmark of the third generation of computers.
Transistors were miniaturized and placed on silicon chips, called semiconductors, which drastically increased the speed and efficiency of computers.
Much smaller and cheaper compared to the second generation computer
IC Integrated circuit
example of computer IBM 360 IBM 370.
During this generation SSI, MSI, and LSI technology
were used.
SSI – Small Scale Integration
MSI- Medium Scale Integration
LSI- Large Scale Integration
The Fourth Generation
The microprocessor brought the fourth generation of computers, as thousands of integrated circuits were built onto a single silicon chip. VLSI technology was used during this generation.
As these small computers became more powerful, they could be linked together to form networks, which eventually led to the development of the Internet.
Fourth-generation computers also saw the development of GUIs, the mouse, and handheld devices.
The desktop computer
came into the market.
The Fifth Generation
• Based on Artificial Intelligence (AI).
• Still in development.
• The use of parallel processing and superconductors is helping to make artificial intelligence a reality.
• The goal is to develop devices that respond to natural language input and are capable of learning and self-organization.
• There are some applications, such as voice recognition, that are being used today
Computer Inputs
An input device is a piece of computer hardware equipment used to provide data and control signals to an information processing system such as a computer or information appliance. Examples of input devices include keyboards, mouse, scanners, digital cameras, joysticks, and microphones.
Computer Outputs
The devices which are used to provide us valuable information called as an output device. There are two forms of output. Which areas below,
Hard Copy
The hard copy is the result that is touchable as well as carriable. One can also read the contents of a hard copy. For example, print out from a printer.
Soft copy
The result from the computer which is only readable, audible but not touchable, or carriable from place to place is called soft copy. For example, a result viewed on a monitor or output from the speaker.
Monitor
A monitor is an output device that creates a soft copy. It produces text or images on the screen. There are different types of monitor designed and used from period to period which are explained below
Monochrome monitor
This is a type of CRT (cathode ray tube) monitor used mostly in the early days from 1965 to 1980 before color monitors come into existence. As the name goes it supports a single color at a single time. One color in the background and one color in the foreground (Mono means single and Chrome means color).
Color graphics adaptor CGA
This was designed by IBM in the year 1981. This was the first color graphics card
HGA
it stands for Hercules graphics adaptor. This was developed by Hercules Computer technology in the year 1982.
EGA
It stands for an enhanced graphics adaptor. This was developed by IBM in the year 1984. It has color capabilities.
VGA
It stands for video graphic adaptor and was introduced by IBM in the year 1987.
SVGA
Super video graphics adaptor designed by a group of American companies in the year 1988. This was more powerful than VGA.
LCD
it stands for liquid crystal display. This is the advanced version of the visual system of a computer flat panel display.
LED
light-emitting diode.